Orionid Meteor Shower Peaks October 21-23, 2025
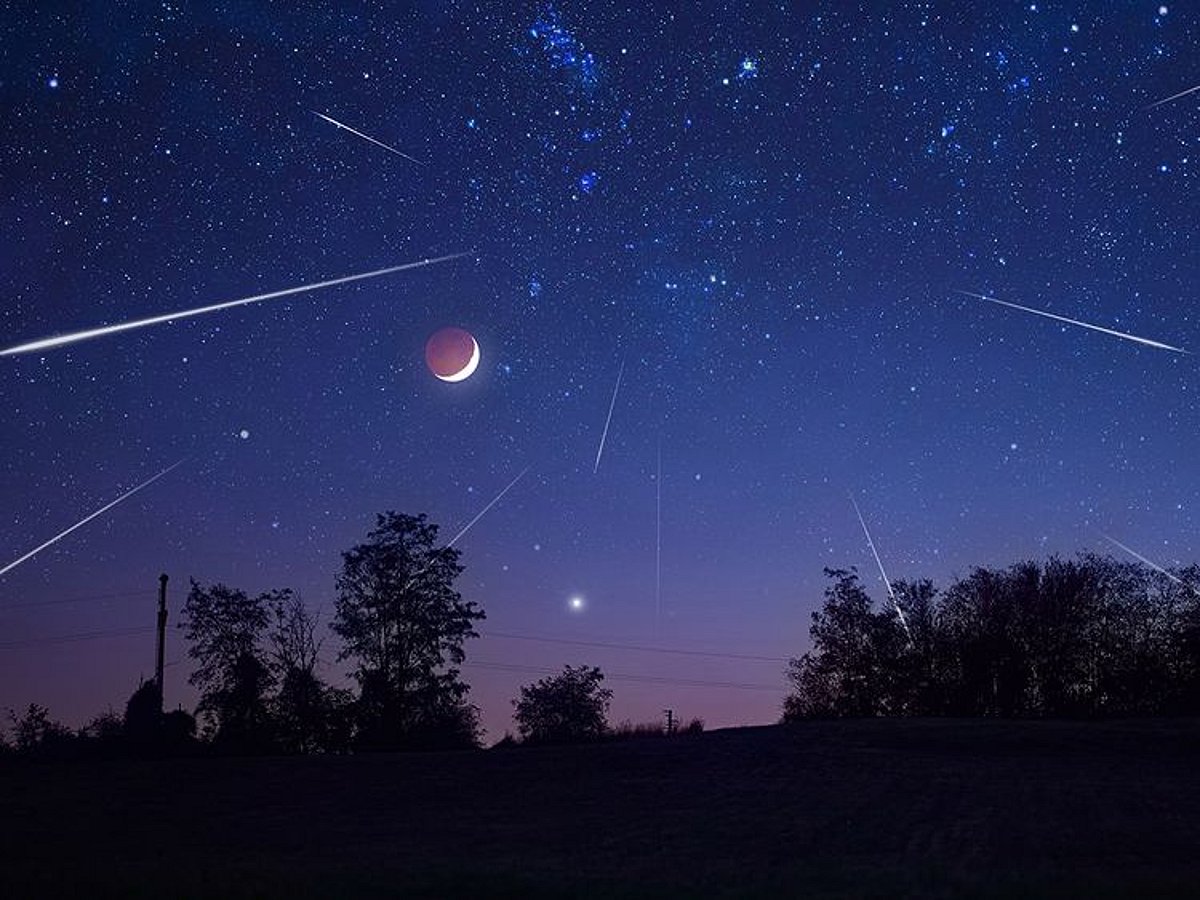
A captivating celestial event is on the horizon as the Orionid meteor shower approaches its peak from October 21 to 23, 2025. This annual phenomenon promises a stunning display of bright meteors for both seasoned astronomers and casual stargazers, particularly during the early morning hours when the sky is at its darkest.
What to Expect During the Orionid Meteor Shower
The Orionid meteor shower is active from October 2 to November 7 each year, and it is renowned for its fast-moving meteors, which can travel at speeds of up to 148,000 miles per hour (approximately 41 miles per second). These meteors appear to radiate from the constellation Orion, specifically near the bright star Betelgeuse, which serves as a guide for observers.
The best time to view the meteors is during the pre-dawn hours, when Orion is positioned high in the southern sky. This year, the peak coincides with a new moon on October 21, resulting in optimal viewing conditions with minimal light interference from the moon.
The Science Behind the Orionids
The Orionid meteor shower is caused by debris left in the wake of Halley’s Comet (officially known as comet 1P/Halley). As Earth orbits the Sun, it passes through this trail of cometary dust and particles. When these fragments enter the atmosphere, they burn up, creating bright streaks of light that we observe as meteors.
Halley’s Comet has a 76-year orbit and last passed near Earth in 1986. It will return in 2061, producing two meteor showers annually: the Eta Aquarids in May and the Orionids in October. The Orionids are particularly notable for their brightness and speed, making them a favorite among skywatchers.
Viewing Tips for the Best Experience
To fully enjoy the Orionid meteor shower, it is advisable to find a dark, open area away from city lights. Allow your eyes about 20 to 30 minutes to adjust to the darkness for optimal viewing. Under ideal conditions, observers can expect to see around 20 meteors per hour, although this number may vary depending on location and weather conditions.
The Orionids are visible from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, making this an accessible event for skywatchers around the world.
Conclusion
The 2025 Orionid meteor shower presents a remarkable opportunity for anyone interested in experiencing the beauty of the night sky. With its peak occurring during a new moon, conditions are perfect for witnessing this natural spectacle. Prepare to be amazed by the bright meteors that will light up the sky from late October 20 through 23.
FAQs
When is the best time to see the Orionid meteor shower?
The best time to view the Orionid meteor shower is during the pre-dawn hours, particularly between 1 AM and dawn, when the constellation Orion is high in the sky.
How fast do the Orionid meteors travel?
Orionid meteors can travel at speeds of up to 148,000 miles per hour, which is approximately 41 miles per second.
What causes the Orionid meteor shower?
The Orionid meteor shower is caused by Earth passing through a trail of debris left by Halley’s Comet, which burns up upon entering the atmosphere, creating bright meteors.
The Orionid meteor shower is one of the most anticipated celestial events of the year, attracting attention from both amateur and professional astronomers. Its origins from Halley’s Comet add a historical significance, as this comet has been observed for centuries, with records dating back to 240 BC. The connection to such a well-known comet enhances the allure of the Orionids, as it serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of our solar system.
In addition to their speed and brightness, the Orionid meteors are known for their colorful displays, often appearing in shades of green, yellow, and orange. This variety in color is due to the different chemical compositions of the meteoroids. As they disintegrate in the atmosphere, the varying elements produce distinct hues, adding to the visual spectacle of the meteor shower. Observers are encouraged to share their experiences and photographs, contributing to a sense of community among stargazers worldwide.
As the 2025 event approaches, many astronomy clubs and organizations may host viewing parties and educational sessions to enhance public engagement with this natural phenomenon. These gatherings can provide valuable insights into meteor showers and the science behind them, fostering a greater appreciation for the wonders of the night sky.
Also Read:
Orionid Meteor Shower Peaks Over UAE Skies Tuesday Morning